 Before we dive into solutions, let's separate solutions from other types
of mixtures. Solutions are groups of molecules that are mixed up in a
completely even distribution. Hmmm. Not the easiest way to say it.
Scientists say that solutions are homogenous systems.
Other types of mixtures can have a little higher concentration on one
side of the liquid when compared to the other side. Solutions have an
even concentration throughout the system. An example: Sugar in water vs.
Sand in water. Sugar dissolves and is spread throughout the glass of
water.
Before we dive into solutions, let's separate solutions from other types
of mixtures. Solutions are groups of molecules that are mixed up in a
completely even distribution. Hmmm. Not the easiest way to say it.
Scientists say that solutions are homogenous systems.
Other types of mixtures can have a little higher concentration on one
side of the liquid when compared to the other side. Solutions have an
even concentration throughout the system. An example: Sugar in water vs.
Sand in water. Sugar dissolves and is spread throughout the glass of
water. Solutions and Mixtures
 Before we dive into solutions, let's separate solutions from other types
of mixtures. Solutions are groups of molecules that are mixed up in a
completely even distribution. Hmmm. Not the easiest way to say it.
Scientists say that solutions are homogenous systems.
Other types of mixtures can have a little higher concentration on one
side of the liquid when compared to the other side. Solutions have an
even concentration throughout the system. An example: Sugar in water vs.
Sand in water. Sugar dissolves and is spread throughout the glass of
water.
Before we dive into solutions, let's separate solutions from other types
of mixtures. Solutions are groups of molecules that are mixed up in a
completely even distribution. Hmmm. Not the easiest way to say it.
Scientists say that solutions are homogenous systems.
Other types of mixtures can have a little higher concentration on one
side of the liquid when compared to the other side. Solutions have an
even concentration throughout the system. An example: Sugar in water vs.
Sand in water. Sugar dissolves and is spread throughout the glass of
water. Kingdoms - Slideshow

Why would we start a slideshow about kingdoms with an image of the Earth? We want you to realize that the Earth is the only place that has known life. We're not even talking about aliens. Neither microscopic organisms nor complex molecules have been discovered on another planet or moon (or dwarf planet). Our planet is very special and unique.
The living organisms of Earth are broken down into two large groupings. You will hear about the prokaryotes (cells without a nucleus) and eukaryotes (cells with a nucleus). This original domain breakdown was even larger than kingdoms. Most of the kingdoms we discuss will be in the domain Eukarya.
Three Domains - Kingdoms Slideshow

The five traditional kingdoms included Monera that were the prokaryotic organisms. As more evidence about species has been uncovered, Monera became two separate domains (Bacteria and Archaea). The third domain includes the four eukaryote kingdoms of protists, plants, fungi, and animals.
If you look at the image above, you will see examples of species from each kingdom. Moving from left to right we have the prokaryotes, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. You are from the kingdom Animalia and are classified as a placental mammal.
Prokaryote Organisms - Kingdoms Slideshow
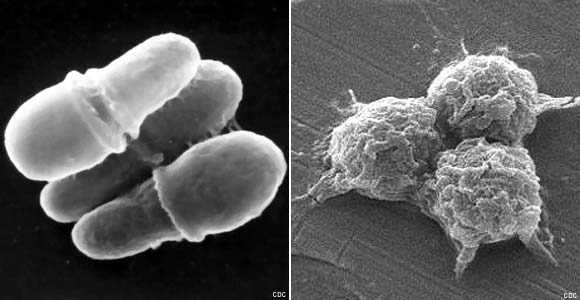
As scientists have learned more about microscopic organisms and prokaryote species, biological classification has changed. Even though bacteria and archaebacteria
are incredibly simple and don't even have nuclear membranes, they make
up two major domains. These are the simplest creatures on Earth (and
the most difficult to see). They might float in the oceans or freshwater
locations. They are even found in your bodies. If they are in your
bodies, they might be diseases trying to infect you.
Kingdom Protoctista - Kingdoms Slideshow

Protists are still microscopic organisms but much more advanced than the prokaryotic species we just talked about. You'll probably see many examples of these species in biology class. Amoebas, algae, or paramecium might wind up under your microscopes. If you want to see some on your own, get a small sample of pond water and look at all of the wee creatures.
Lichen - Kingdoms Slideshow

We love lichen at Biology4Kids. They are cool symbiotic organisms that are made of fungi and photosynthetic algae. While they might not be a kingdom on their own, they are worth a comment.
Neither of the two species can survive on their own and as they grow, lichen form an amazing variety of shapes. You will usually find them in very clean areas where rocks or plant debris are being decomposed.
Neither of the two species can survive on their own and as they grow, lichen form an amazing variety of shapes. You will usually find them in very clean areas where rocks or plant debris are being decomposed.
Kingdom Fungi - Kingdoms Slideshow

Fungi species were once classified as plants.
Scientists quickly looked at fungus species and noticed that they didn't
use photosynthesis to generate their own energy. They are heterotrophs
(organisms that eat other organic objects for energy). As time has
passed, evidence has shown fungi species to be even more like animals
than plants. Fungi are all about decomposition. Mushrooms break down
rotting trees in forests. Mold breaks down food as it gets older.
Kingdom Plantae - Kingdoms Slideshow

We're going to break plants down into two groups for this slideshow. All plants are in the same kingdom but there are so many species we thought you deserve two slides. This slide is looking at some very basic plants.
The above image shows you examples of mosses, horsetails, and ferns. These are all plants that do not create seeds when they reproduce. Let's look closer at each type of plant.
Kingdom Plantae - Kingdoms Slideshow

The next set of plants in our show has developed the ability to produce seeds. Gymnosperms such as conifers and cycads produce naked seeds. Angiosperms that include all flowering plants are able to produce seeds with one or two seeds coats.
Conifers produce cones that hold seeds until they are ready to release into the wind. They are able to sexually reproduce when wind spreads pollen to neighboring cones. Flowering plants use a variety of methods to reproduce. While some species use wind, many others rely on insects to spread pollen from one flower to another. Some species are so specialized that they can only be pollinated by one species of insect. If that insect is not around, the plant species will eventually become extinct.
Image Credit: Andrew Rader Studios
Courtesy:http://www.biology4kids.com
Conifers produce cones that hold seeds until they are ready to release into the wind. They are able to sexually reproduce when wind spreads pollen to neighboring cones. Flowering plants use a variety of methods to reproduce. While some species use wind, many others rely on insects to spread pollen from one flower to another. Some species are so specialized that they can only be pollinated by one species of insect. If that insect is not around, the plant species will eventually become extinct.
Image Credit: Andrew Rader Studios
Courtesy:http://www.biology4kids.com
Kingdom Animalia - Kingdoms Slideshow

Since we broke up the plants into two groups, we decided to break the animal kingdom into two groups. This slide highlights animals called invertebrates. You need to know that there are many more invertebrates in the world than vertebrates. Not only are there greater numbers, but there are also many more species.
Invertebrates include any animal that does not have vertebrae (backbone). Here's a short list of invertebrates:
Kingdom Animalia - Kingdoms Slideshow
Here we are. The vertebrates of the animal kingdom are most like you. We all have backbones and a skull
to protect a brain and spinal cord. There are five basic groups of
vertebrates. While you know you are a mammal, there are also fish,
amphibians, reptiles, and birds.
Classification of vertebrate species is based on common traits.
Variety of Life - Kingdoms Slideshow
Let's finish off this slideshow with a little reflection. Every species
on Earth depends on the other species. You might not think about it
while you sit in class, but you depend on fungi to decompose trees in the Pacific Northwest. Insects in the Amazon jungle depend on forests
in Africa to filter the air that will eventually move across the
Pacific Ocean. We all need to work together to maintain our delicate
ecosystems.
FOOD CHAINS
 Another Link in the Food Chain
Producers
Another Link in the Food Chain
ProducersEveryone plays a specific role in the food chain of life. You might be a human thinking they are king of the hill or you might be a bacterium under the feet. You are very important to the survival of the system no matter what role you play. As you study more about ecosystems and cycles in life, you will see the terms food chains and food webs.
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
PART I: THE SUN AND LIGHT
 Super basic process of photosynthesis Not all of the light from the Sun makes it to the surface of the Earth. Even the light that does make it here is reflected and spread out. The little light that does make it here is enough for the plants of the world to survive and go through the process of photosynthesis.
Super basic process of photosynthesis Not all of the light from the Sun makes it to the surface of the Earth. Even the light that does make it here is reflected and spread out. The little light that does make it here is enough for the plants of the world to survive and go through the process of photosynthesis.
 Super basic process of photosynthesis Not all of the light from the Sun makes it to the surface of the Earth. Even the light that does make it here is reflected and spread out. The little light that does make it here is enough for the plants of the world to survive and go through the process of photosynthesis.
Super basic process of photosynthesis Not all of the light from the Sun makes it to the surface of the Earth. Even the light that does make it here is reflected and spread out. The little light that does make it here is enough for the plants of the world to survive and go through the process of photosynthesis.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




